Introduction to information communication technology(ICT) (ii)
Notes
SOFTWARE
Software is detailed step-by-step sequence of instructions known as program which guide
computer hardware. A computer program is a sequence of instructions that tell the computer
hardware what to do. Programs are written in (programming) languages, which consist of a
set of symbols combined according to a given syntax.
A program must be in main memory (RAM) to be executed. These invisible, intangible components
of a computer that direct and control the operations of the hardware when processing data are
referred to as software.
Software is classified into two major types: System and Application software.
System Software
System software consists of programs that coordinates the activities of hardware and other
programs. System software is designed for a specific CPU and hardware class. The combination
of a particular hardware configuration and operating system is called a computer platform. These
programs manage the �behind the scenes� operation of the computer.
Examples
Utility Programs - Utility programs often come installed in computer systems or packaged with
operating systems. Utilities can also be purchased individually. Utility programs perform useful
tasks, such as virus detection, tracking computer jobs and compressing data.
Language processors � Compilers and interpreters
Application Software
Applications software include programs designed to help end users solve particular problems
using the computer or to perform specific tasks.
Sources of software
|
|
Proprietary Software |
|
Off-the-shelf |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
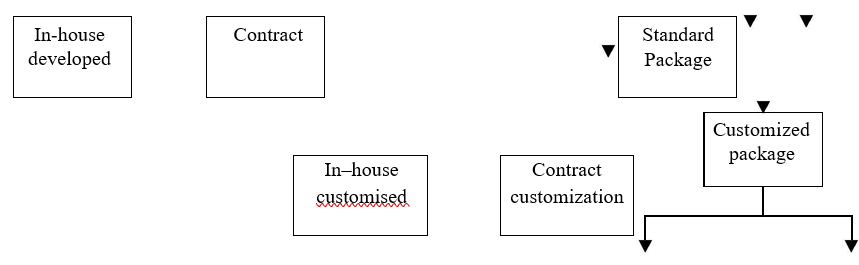
Proprietary Software
Is a computer software which is
legal property of one party. The terms of use for other parties is defined by
contracts or licensing agreements.
Advantages of proprietary software
•
You can get exactly what you need in terms of
reports, features etc.
•
Being involved in development offers a further
level in control over results.
•
There is more flexibility in making
modifications that may be required to counteract a new initiative by a
competitor or to meet new supplier or customer requirements. A merger with
another firm or an acquisition will also necessitate software changes to meet
new business needs.
Disadvantages of proprietary software
•
It can take a long time and significant
resources to develop required features.
•
In house system development staff may become
hard pressed to provide the required level of ongoing support and maintenance
because of pressure to get soft ware
Off-the-Shelf Software
Off-the-shelf is a term for
software or hardware, generally technology or computer products that are
ready-made and available for sale, lease or license to the general public. Advantages of off-the-shelf software
-
The initial cost is lower since the software
firm is able to spread the development costs over a large number of customers.
-
There is lower risk that the software will fail
to meet the basic business needs
-
You can analyze existing features and
performance of the package
-
Package is likely to be of high quality since
many customer firms have tested the software and helped identify many of its
bugs.
Disadvantages of off-the-shelf software
-
An organization may have to pay for features
that are not required or never used.
-
The software may lack important features, thus
requiring future modifications or customization. This can be very expensive
because users must adopt future releases of the software.
-
Software may not match current work processes
and data standards.
Application software is further
classified into general-purpose software and applications which include:
-
Word processing – Create, edit and
print text documents, e.g. MS Word and Word Perfect.
-
Spreadsheets – Provide a wide range
of built-in functions for statistical, logical, financial, database, graphics,
data and time calculations, e.g. Lotus 1-2-3, Excel and Quattro Pro.
-
Database management systems (DBMS) –
Store, manipulate and retrieve data. e.g. Access, FoxPro and dBase.
-
Online Information Services – Obtain
a broad range of information from commercial services. e.g. America Online and
CompuServe
-
Communications - Ms Outlook for
email
-
Browsers e.g Internet Explorer and Eudora
-
Graphics – Develop graphs,
illustrations and drawings. e.g. PaintShop, FreeHand and Corel
-
Project Management – Plan, schedule,
allocate and control people and resources needed to complete a project
according to schedule. e.g. Project for Windows and Time Line.
-
Financial Management – Provide
income and expense tracking and reporting to monitor and plan budgets, e.g.
Quicken
-
Desktop publishing - used to create
high-quality printed output including text and graphics; various styles of
pages can be laid out; art and text from other programs can also be integrated
into published pages, e.g. PageMaker and Publisher. - Presentation packages like MS
PowerPoint
Note
A software suite, such as
Microsoft Office, offers a collection of powerful programs including word
processing, spreadsheet, database, graphics among others. The programs in a
software suite are designed to be used together. In addition, the commands, t icons
and procedures are the same for all programs in the suite.
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES
Programming languages are
collections of commands, statements and words that are combined using a
particular syntax, or rules, to write both systems and application software.
This results in meaningful instructions to the CPU.
Generations of programming languages
Machine Language (1st Generation Languages)
A machine language consists of
binary digit, that is, zeroes (0) and ones (1). Instructions and addresses are
written in binary (0,1) code. Binary is the only “language” a CPU can
understand. The CPU directly interprets and executes this language, therefore
making its execution of instructions fast. Machine language programs directly
instructed the computer hardware, so they were not portable. That is, a program
written for computer model A could not be run on computer model B without being
rewritten. All software in other languages must ultimately be translated down
to machine language form. The translation process makes the other languages
slower.
Advantage
• The
only advantage is that programs of machine languages run very fast because no
translation program is required for the CPU.
Disadvantages
• It
is very difficult to programs in machine language. The programmer has to know
details of hardware to write the program.
• The
programmer has to remember a lot of codes to write a program, which sometimes
result in errors.
• It
is difficult to debug a program.
Assembly Language (2nd Generation
Languages)
Uses symbols and codes instead of
binary digits to represent program instructions. It is a symbolic language
meaning that instructions and addresses are written using alphanumeric labels
that are meaningful to the programmer.
The resulting programs still
directly instruct the computer hardware. For example, an assembly language
instruction might move a piece of data stored at a particular location in RAM
into a particular location on the CPU. Therefore, like their first generation
counterparts, second generation programs were not easily portable.
Assembly languages were designed
to run in a small amount of RAM. Furthermore, they are low level languages;
that is the instructions directly manipulate the hardware. Therefore, programs
written in assembly language execute efficiently and quickly. As a result, more
systems software is still written using assembly languages.
The language has a one-to-one
mapping with machine instructions but has macros added to it. A macro is a
group of multiple machine instructions, which are considered as one instruction
in assembly language. A macro performs a specific task, for example adding and
subtracting. A one-toone mapping means that for every assembly instruction,
there is corresponding single or multiple instructions in machine language.
An assembler is used to translate
the assembly language statements into machine language.
Advantages:
-
The symbolic programming of Assembly Language is
easier to understand and saves a lot of time and effort of the programmer.
-
It is easier to correct errors and modify
program instructions.
-
Assembly Language has the same efficiency of
execution as the machine level language This is because this is a one-to-one
translator between assembly language program and its corresponding machine
language program.
Disadvantages:
-
One of the major disadvantages is that assembly
language is machine dependent. A program written for one computer might not run
in other computers with a different hardware configuration.
High-level languages (3rd Generation
Languages)
Third generation languages are
easier to learn and use than were earlier generations. Thus programmers are
more productive when using third generation languages. For most applications,
this increased productivity and compensates for the decrease in speed and
efficiency of the resulting programs. Furthermore, programs written in third
generation languages are portable, that is, a program written to run on a
particular type of computer can be run with little or no modification on
another type of computer. Portability is possible because third generation
languages are “high-level languages”; that is, instructions do not directly
manipulate the computer hardware.
Third generation languages are
sometimes referred to as “procedural” languages since program instructions, must give the computer detailed
instructions of how to reach the desired result. High-level languages incorporated
greater use of symbolic code. Its statements are more English– like, for
example print, get and while. They are easier to learn but the resulting
program is slower in execution. Examples
include Basic, Cobol, C and Fortran. They have first to be compiled (translated
into corresponding machine language statements) through the use of compilers
Advantages of High Level Languages
-
Higher level languages have a major advantage
over machine and assembly languages since they
are easy to learn and use.
-
Are portable
Fourth Generation Languages (4GLs)
Fourth generation languages are
even easier to use, and more English-like, than are third generation languages.
Fourth generation languages are sometimes referred to as “nonprocedural”, since
programmes tell the computer what it needs to accomplish, but do not provide
detailed instructions as to how it should accomplish it. Since fourth
generation languages concentrate on the output, not procedural details, they
are more easily used by people who are not computer specialists, that is, by
end users.
Many of the first fourth
generation languages were connected with particular database management
systems. These languages were called Query Languages since they allow people to
retrieve information from databases. Structured query language, SQL, is a current
fourth generation language used to access many databases. There are also some
statistical fourth generation languages, such as SAS and SPSS.
Some fourth generation languages,
such as Visual C++, Visual Basic, or PowerBuilder are targeted to more
knowledgeable users, since they are more complex to use. Visual programming
languages, such as visual basic, use windows, icons, and pull down menus to
make programming easier and more intuitive.
Object Oriented Programming
First, second, third and fourth
generation programming languages were used to construct programs that contained
procedures to perform operations, such as draw or display, on data elements
defined in a file.
Object oriented programs
consist of objects, such as a time card, that include descriptions of the data
relevant to the object, as well as the operations that can be done on that
data. For example, included in the time card object, would be descriptions of
such data such as employee name, hourly rate, start time and. The time card
object would also contain descriptions of such operations as calculating total
hours worked or calculating total pay.
Language translators
Although machine language is the
only language the CPU understands, it is rarely used anymore since it is so
difficult to use. Every program that is not written in machine language must be
translated into machine language before it can be executed. This is done by a
category of system software called language translation software. These are
programs that convert the code originally written by the programmer, called
source code, into its equivalent machine language program, called object code.
There are two main types of
language translators: interpreters and compilers.
Interpreters
While a program is running,
interpreters read, translate, and execute one statement of the program at a
time. The interpreter displays any errors immediately on the monitor.
Interpreter are very useful for people learning how to program or debugging a
program. However, the line-by-line translation adds significant overhead to the
program execution time leading to slow execution.
Compilers
A compiler uses a language
translation program that converts the entire source program into object code,
known as an object module, at one time. The object module is stored and it is
the module that executes when the program runs. The program does not have to be
compiled again until changes are made in the source code.
Software trends and issues
Open source software coming to
the scene: This is software that is freely available to anyone and can be
easily modified. The use of open source software has increased dramatically due
to the World Wide Web. Users can download the source code from web sites. Open
source software is often more reliable than commercial software because there
are many users collaborating to fix problems. The biggest problem with open
source software is the lack of formal technical support. However, some
companies that package open source software with various add-ons and sell it
with support are addressing this. An example of this is Red Hat Linux operating
system.
ICT PERSONNEL AND INFORMATION COMMUNICATION
TECHNOLOGY HIERARCHY.
The organisation of ICT department
ICT Department functions
a) Development,
ongoing operation and maintenance of information systems
b) Advisor
to ICT users throughout the organisation
c) Catalyst
for improving operations through system enhancements/ new systems development
d) Co-ordinating
systems integration in the organisation.
e) Establishing
standards, policy, and procedures relating to ICT.
f) Evaluating
and selecting hardware and software.
g) Co-ordinating
end-user education.
Officers in ICT department
•
IT Manager/Director
•
Systems analysts
•
Programmers - system and applications
•
Database administrator
•
Network administrator
• Librarian
